Have you heard of the term Intellectual Property? Anything that is an intangible form of creation yet a valuable mind creation is called Intellectual Property.
3 Types of Intellectual Property
- Patent
- Trademark
- Copyright
In this blog, we will focus on everything that you need to know about trademarks.
Table of Contents (Click to jump to a particular section)
What Is A Trademark And What Does It Protect?
Key Important Features Of A Trademark
Inherent v/s Acquired Distinctiveness of Trademarks
What are the types of trademarks?
Introduction to Trademarks in 2022
How do you instantly identify a Microsoft logo, an apple iPhone, a Domino’s pizza or a Starbucks coffee mug?
By their unique trademarked logos.
A logo can be the sole driving force behind building a brand’s image, and this is because people identify a brand/company by looking at its trademark.
- While thinking of Jaguar luxury cars, we instantly think of the silver leaping jaguar cat.
- While thinking of Adidas, we immediately think of the Trefoil Logo.
Yes, all the magic of their unique and eye-catching trademarks has helped these brands to make big in the global markets.
What Is A Trademark And What Does It Protect?
Trademark is a logo/symbol/phrase/slogan that protects your company’s brand, authenticity, and market image.
But how does a trademark protect your brand?
- By providing a unique face/identity to the goods and services of your company.
- By preventing anyone else from using your unique logo or providing goods & services under the same logo.
Key Important Features Of A Trademark
| Key Trademark Features | Meaning | Examples |
| Distinctive | The consumers must be able to distinctively identify the trademark and distinguish it from other marks. There must be no scope of any likelihood of confusion. | Mustang Cars |
| Non-Descriptive | The trademark should not provide an immediate idea of the goods/services to be sold, their features, quality or components. Suppose a brand sells cotton t-shirts, then it can’t trademark “Cotton T-Shirts,” i.e., a word that merely describes the product/service cannot be trademarked. | “Cheesy Pizza” is too descriptive, “Domino’s” is suggestive and non-descriptive. |
| Suggestive | Provide a suggestion or reference to the products or services. | E.g. Microsoft (microcomputer software) |
* Generally, descriptive trademarks can’t be registered. But there is one exception. If a person/company has been using the trademark for a very long time, such that:
- The primary meaning of the mark is lost
- The trademark has acquired a strong uniqueness.
For e.g., International Business Machine (IBM).
Inherent v/s Acquired Distinctiveness of Trademarks
The distinctiveness of a trademark can be: Natural/Inherent or Acquired.
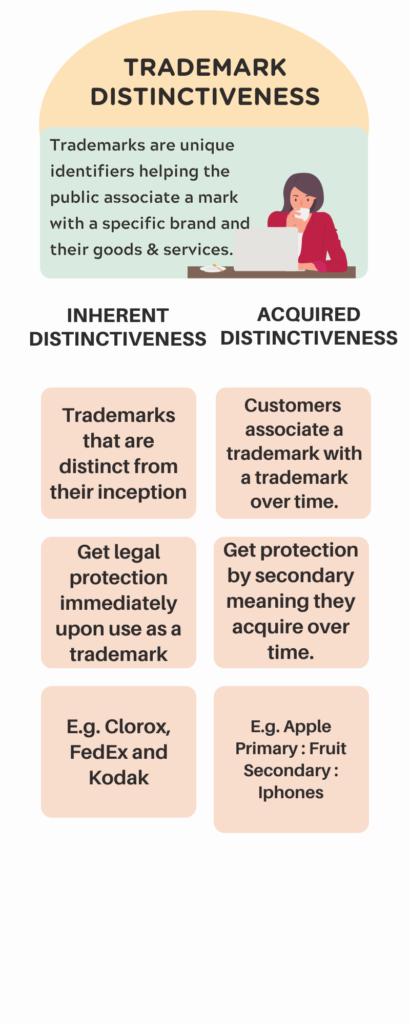
So, 3 things are clear by now:
- A trademark is a unique identifier that helps to build a loyal customer base and protect a brand’s market image.
- Almost all the big brand names have invested heavily in their trademarks.
- A trademark is not limited to a catchy phrase or attractive logo (McDonald’s) or a slogan (Just Do It – Nike). Audio, smell, and taste as well can be registered as trademarks.
Really?
Yes, there exist more than 10 types of trademarks. The next section contains a complete table of types of trademarks.
What are the types of trademarks?
| Types of Trademarks | Description | Requirements for Registration | Trademark Examples |
| Product Trademark | Used to identify the origin of a product/good and distinguish it from competitors. | Unique & distinctive service Non-descriptive No likelihood of confusion | Starbucks Levis Adidas Nike |
| Service Trademark | Used to identify the origin of a service and distinguish it from competitors. | Unique & distinctive service Non-descriptive No likelihood of confusion | Google Qatar Airways FedEx |
| Certification Trademark | Certification trademarks certify the nature and origin of the goods and services to which it has been given. It includes: Region or location Materials used Mode of manufacturing Product quality. | Standards Exclusivity of use Objectivity Non-discrimination A famous example of a certification mark is the EnergyStar logo on appliances that states that the product meets the established standards. | ISI Trademark FPO (Farmer Producer Organization) Trademark AG Mark |
| Scent/Smell Trademark | An olfactory or scent trademark is the unique smell capable of identifying a product. Countries like the USA, European Union (EU), Canada, Australia, etc., permit scent trademarks. | Non functionality: Registerable if you prove that the smell is a key identifier for the product with no practical function. Distinctiveness of the smell | Eucalyptus-scented golf tee- trademarked in Australia. Flowery musk scent (Verizon stores) – trademarked in USA. Piña colada scent to coat ukuleles – trademarked in USA |
| Shape Trademark | 3-D Trademarks that protects the shape of the product, brand, logo, label, or tag. | The particular product should have a 3-D trademark view. In case the trademark registrar is not satisfied, the applicant will need to provide 5 different views along with describing the shape mark by words. | The shape of zippo lighters. Coca-Cola bottle. |
| Sound Trademark | Non-conventional trademark where sound helps in uniquely identifying the commercial origin of goods or services. | The sound mark can be produced in MP3 format with a graphical representation of its notations. A 30-second MP3 reproduction A visual representation of the sound, like waveform/note sheet/musical notations identifying where the notes lie. A clear description of the sound, e.g., listening to the notes in the sound. Factual distinctiveness and should not be generic in nature. | McDonalds’ classic “I’m Lovin it” sound. Airtel’s signature ringtone Yahoo Yodel Nokia Guitar Sound MGM – Entertainment – Roaring Lion Audi’s heart-beat sound logo. |
| Motion Trademarks | 3-D/moving trademarks having a combination of moving visuals with audio. | A textual explanation of the trademark A drawing showing a single point in the movement or a square drawing with maximum 5 freeze frames that shows various movement directions. | Microsoft’s motion trademark. |
| Pattern Trademarks | Patterns that are unique enough to identify the goods or services as originating from a specific brand. | Distinctiveness of the pattern, i.e., it should be identifiable in the minds of the consumers with a brand’s goods or services. | Repeating hexagonal shapes either printed or stitched on the inner lining of shoe uppers. Repeating patterns of the word DIOR for luxury cosmetics and perfumes. |
| Color Trademarks | Particular shades and hues of a color registered to a particular brand/business. | Can be graphically represented Unique and distinctive | Tiffany blue by Tiffany & Co. Target’s Red. |
| Taste Trademarks | Taste or flavor marks able to identify the products by the consumers. | Non-functionality Distinctiveness | No taste marks has been registered yet. |
What makes a trademark?
Everything ranging from:
- The color scheme
- Logo
- Shape (circular/square/rectangle)
- Slogan length
- Language
- Uniqueness
What does a trademark protect?
- A brand’s market image/reputation by preventing competitors from using a similar or identical trademark.
- Brand’s goods or services from being copied or sold using a similar trademark name or logo.
- Consumers’ confidence in the brand by avoiding the likelihood of confusion.
Along with the protection from infringement under Trademarks Act, a trademark also provides:
- A unique identity to the brand.
- Notice to the consumers about the brand’s trademark and so its goods/services.
- Exclusive trademark rights to sell the goods or services across the nation.
- Sue the trademark infringer.
- Prevent the import of mock goods into the nation.
- File for a trademark abroad (having a registered national trademark aggravates the process of registering a trademark in a foreign nation).
How does a Trademark work?
A trademark works by providing the exclusive trademark rights to the trademark owner to initiate a lawsuit against anyone trying to infringe their rights by:
- Illegally trying to register a similar/identical trademark
- Selling goods/services under a similar/identical trademark and illegally reaping the revenue benefits from the trademark owner.
Get Your Brand Trademarked With TMReady
TMReady is your best buddy for any trademark-related services. Whether you want to perform a professional trademark search or register your trademark or keep a continuous watch on your mark for infringement.
Get assistance by our professional trademark attorneys here.
