In an increasingly globalized economy, businesses are constantly seeking efficient ways to protect their intellectual property across borders. Trademarks, as crucial brand assets, demand global protection to prevent unauthorized use and infringement in international markets. One of the most effective tools for achieving this is the Madrid Protocol.
This blog explains what is the Madrid Protocol, how the Madrid Protocol system works, its advantages, potential risks, and strategies for effective international trademark protection. We also provide insights into Madrid Protocol trademark search practices and link to relevant, trusted resources.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is the Madrid Protocol?
The Madrid Protocol is an international treaty that allows trademark owners to file a single application for trademark registration in multiple countries. It’s a system managed by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). The Madrid Protocol system, governed by both the Madrid Agreement and Madrid Protocol, offers a simplified and cost-effective way to protect trademarks in foreign markets.
Instead of filing separate applications in each jurisdiction, the system enables applicants to submit one international application through their national IP office. WIPO then forwards the application to the selected foreign IP offices for examination.
As of 2024, there are 131 Madrid Protocol countries, covering over 80% of global trade. This makes it a powerful option for businesses looking to expand their brand globally.
Key Benefits of the Madrid Protocol System
1. One Application, Multiple Jurisdictions
A major benefit of the Madrid Protocol trademark process is the ability to file one application in a single language (English, French, or Spanish) and pay one set of fees. This simplifies the process of seeking protection in multiple countries and eliminates the need to file individual national applications.
2. Cost Efficiency
Using the Madrid Protocol can significantly reduce legal, translation, and administrative costs. For small to mid-sized enterprises, the cost savings can be substantial compared to filing in each country separately. A WIPO report shows consistent annual growth in international filings, with over 65,000 applications submitted in 2023 alone.
3. Streamlined Management
After registration, trademark holders can manage renewals, changes in ownership, or address updates through a centralized system. This saves time and effort, especially for businesses operating in multiple regions.
4. Subsequent Designation
The Madrid Protocol offers flexibility through “subsequent designation.” This means you can extend your trademark protection to additional member countries after the initial registration, without filing a new application.
5. Centralized Tracking Tools
WIPO’s Madrid Monitor and Global Brand Database allow businesses to conduct a Madrid Protocol trademark search, monitor application progress, and identify conflicts, all in one place.
Countries in Madrid Protocol
As of May 2024, the Madrid Protocol countries include major economies like the USA, UK, Canada, EU member states, Japan, China, India, Australia, and many others.
While many major markets are covered, it’s important to note that some countries (e.g., some parts of the Middle East and Africa) are still outside the system. For those regions, national filings remain necessary.
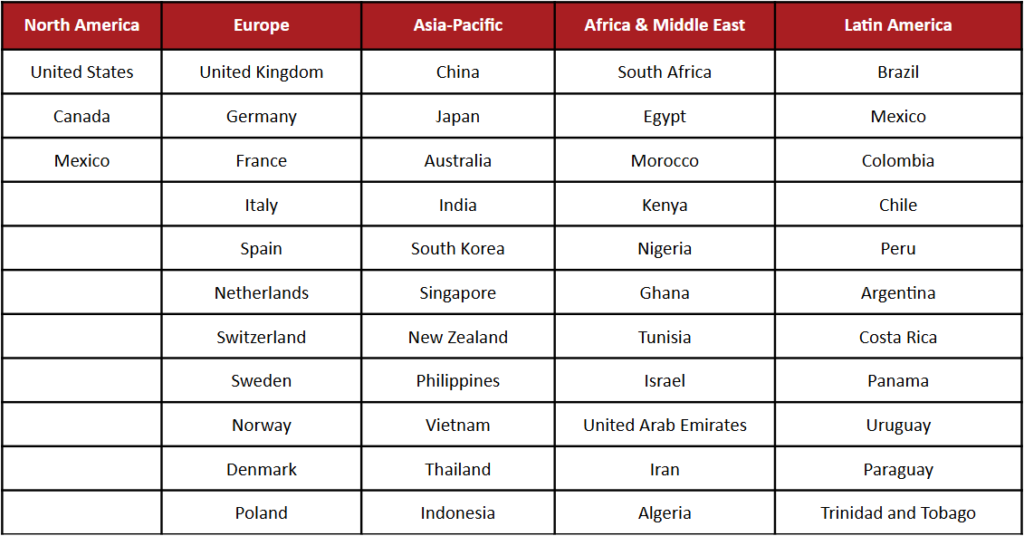
For a complete and updated list of all member countries under the system, please refer to the official Members of the Madrid Union page maintained by WIPO.
Limitations and Risks of Madrid Protocol
While the Madrid Protocol system offers many benefits, it’s not without challenges. Here are the key risks and limitations to be aware of:
1. Dependency on the Base Application
An international registration is tied to the basic trademark application or registration in the applicant’s home country for the first five years. If the base application is cancelled or refused, the international registration is also affected. This vulnerability is known as a “central attack.”
2. Local Examination Still Required
Each designated country examines the application independently. Even though you file one application, every country has its own legal standards and may raise objections or oppositions.
3. Not a Fully Global Solution
While the system covers over 130 countries, it is not universal. Businesses may still need to pursue separate national filings in non-member countries. You should carefully consider your market presence before assuming full global coverage.
4. Procedural Complexity in Some Jurisdictions
Though the system is centralized, legal requirements, like providing local legal representation, responding to refusals, or managing oppositions, still apply in individual countries. These may introduce unexpected costs and delays.
Madrid Protocol Trademark Search: Why It Matters
Conducting a Madrid Protocol trademark search before filing is essential to avoid refusals due to conflicts with existing trademarks. WIPO’s Madrid Monitor and Global Brand Database are excellent tools for:
- Checking availability in target countries
- Identifying similar or identical marks
- Monitoring potential opposition risks
Conducting thorough searches upfront helps minimize refusals and accelerates the registration process.
Best Practices and Strategies
To make the most of the Madrid Protocol trademark process, consider the following best practices:
1. Start with a Strong Base Application
Since your international registration depends on your home application, ensure it’s accurate, defensible, and thoroughly reviewed before filing internationally.
2. Identify Key Markets Strategically
Don’t file in every available country at once. Prioritize the countries where you currently do business or plan to enter within the next 12–24 months. Use subsequent designation for future expansions.
3. Use Official WIPO Tools
Make full use of Madrid Monitor and Global Brand Database to conduct searches, track progress, and manage your portfolio.
4. Prepare for Objections
Even with centralized filing, objections in individual countries are common. Be prepared to engage local legal counsel in complex jurisdictions like the EU, China, or the USA.
5. Stay Updated on Member Countries
The list of countries in Madrid Protocol continues to grow. Regularly check WIPO’s member list to stay updated and plan your international strategy accordingly.
Conclusion
The Madrid Protocol has transformed the way businesses protect their trademarks globally. By consolidating filing processes, reducing costs, and simplifying portfolio management, the system empowers businesses to protect their brand identities more efficiently than ever before.
However, it’s essential to understand both its benefits and its limitations. Conducting a thorough Madrid Protocol trademark search, selecting countries strategically, and maintaining strong base applications are all key to successful international registration.



