The Metaverse combines the elements of social media, online gaming, virtual reality, augmented reality, and blockchain to allow users to interact with one another using avatars. It is expected to expand in size, providing users with varied environments to play, work and socialize. Its usage is not just for people but also for brands to help them engage with their customers and market their products and services. For instance, brands can advertise in the Metaverse or even have customers browse and buy products. These virtual worlds also allow users to buy and sell branded, digital merchandise. With this new digital frontier, safeguarding intellectual property, particularly through trademark application, has become essential.
With the impact Metaverse could have on products and services, businesses must strive to safeguard their Intellectual Property (IP) in the Metaverse domain – especially the usage of Trademarks. Filing a trademark application for virtual products ensures exclusive rights to use those trademarks, preventing others from adopting similar names or logos. The unique nature of the Metaverse introduces legal challenges, making it critical for companies to understand how to protect their trademarks in this space.
This article is a comprehensive discussion on everything you need to know about trademarks in the Metaverse, including their need, how trademarks protect brands in the Metaverse, trademark-related issues in the Metaverse, and the best practices for trademark owners, and more. Let us begin by understanding the concept of the Metaverse.
How has the Metaverse evolved?
The word “Metaverse” was introduced 30 years ago by an American science fiction writer, Neal Town Stephenson, in his 1992 novel, “Snow Crash.” It was part science fiction – part speculation. Fast forward to 30 years after, this concept of an open virtual environment for everyone has become a reality. Currently, many companies are attempting to create the Metaverse or various types of mixed reality environments which combine multiple technologies, such as AI, blockchain, VR, and AR.
At a time when we are realizing the futuristic idea of the Metaverse and its essential technological innovations, one industry is leading the development of this virtual world – the gaming industry. The Metaverse is evolving from two decades of gaming and will be built upon the gaming infrastructure. Since the beginning of the Metaverse talk, game developers have been at the forefront, leading discussions on everything from virtual worlds to digital tokens.
Such is the influence of the gaming industry in the world of Metaverse that one of the prominent gaming companies, Epic Games, received its largest-ever round of fundraising with a $2 billion investment. This fundraiser has set the market capitalization of Epic Games to $31.5 billion.
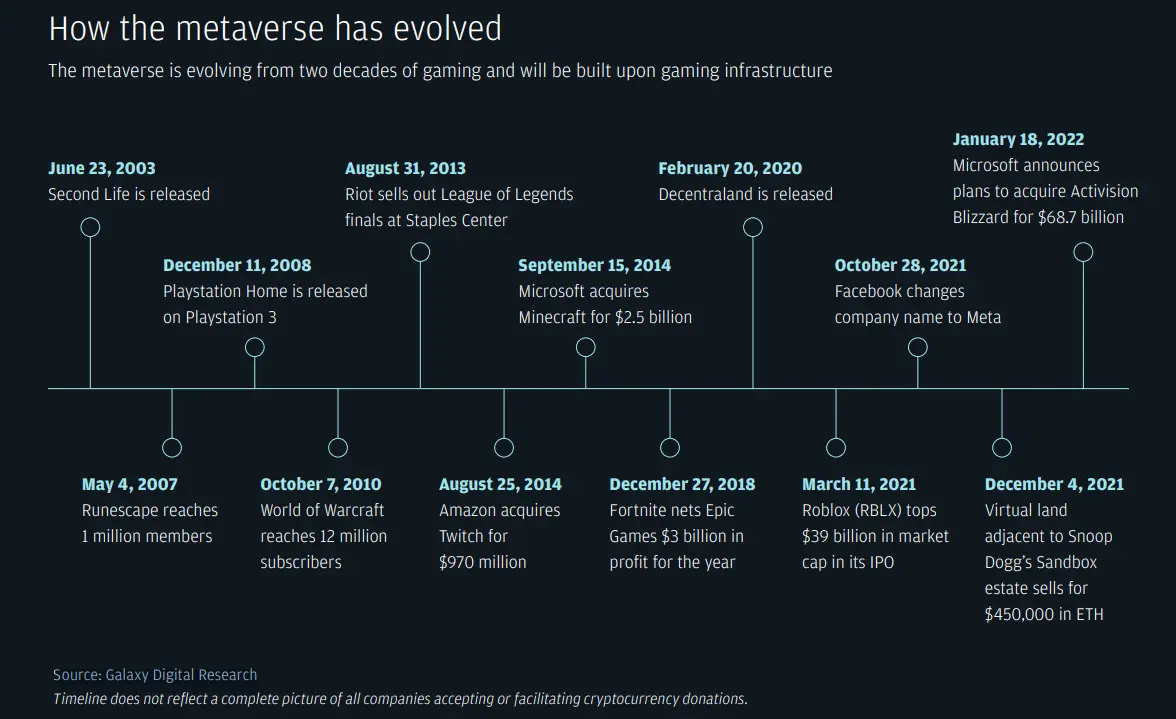
Now, let us have a look at the companies that have been leading the charge in developing the Metaverse.
Who is Developing the Metaverse?
Companies developing the Metaverse are focused on building new innovations and features to enable users to interact with each other efficiently and effectively digitally. The Metaverse companies are at the forefront of transforming the digital world with immersive experiences in the future. The top ten companies developing this digital space are:
- Meta (Previously Facebook)
- NVIDIA
- Epic Games
- Microsoft
- Apple
- Decentraland
- Roblox Corporation
- Unity Software
- Snapchat
- Amazon
Many businesses want to know more about what the Metaverse can accomplish or what their brands can do in this virtual space. The following section will explain the same.
What does the Metaverse mean for Brands?
The Metaverse presents businesses with new opportunities to expand their reach, grow their digital presence, and increase revenue. Many major brands are already planning campaigns for this emerging space. Similar to social platforms, the Metaverse requires brands to adapt their voice and actions to fit the digital environment. For businesses, it’s simply another way to grow, and trademarks are essential for safeguarding their brand from misuse. Trademark registration for the Metaverse is becoming a necessary step, not just a consideration.
Nike – one of the biggest and most famous brands in the world – filed several trademark application late last year, signaling its intention to create and sell virtual sneakers and clothes. It is the clothing company’s first step into the Metaverse. The trademark registrations clearly indicate Nike’s keen interest in capitalizing on the potential of the virtual space.

This is not the first time Nike has explored virtual reality. In May 2019, Nike partnered with “Fortnite,” where the characters wore Nike sneakers. The apparel company is also teaming up with Roblox to create a digital world named “Nikeland,” where users can dress up their avatars in Nike apparel. Moreover, Nike purchased the NFT studio RTFKT, which creates virtual sneakers and other collectibles. In December 2019, Nike secured a patent for “CryptoKicks,” for linking digital assets, such as NFTs, with physical products like sneakers.
Read more about Metaverse and NFT IP rights here. In the next section, we will discuss the best way to protect a brand in the Metaverse through trademarks.
How do Trademarks protect brands in the Metaverse?
Trademarks protect the identity of a company and the reputation of its brand(s), including in the Metaverse. In the Metaverse, where virtual interactions and digital assets dominate, trademark application play a pivotal role in safeguarding brand identity. As businesses expand into this virtual space, protecting their trademarks ensures they maintain control over their brand image and prevent unauthorized use. Some of the perks of using a trademark in the Metaverse are as follows:
- Exclusive Rights: A successful trademark application grants the owner exclusive rights to use the mark in the virtual environment.
- Brand Protection: It helps protect against unauthorized use, ensuring that the brand’s reputation remains intact.
- Legal Enforcement: Registered trademarks provide legal grounds to challenge infringement, both in real life and virtual spaces.
- Consumer Trust: Trademarks assure customers of the authenticity of virtual products, fostering trust and brand loyalty.
- Market Differentiation: A registered trademark helps distinguish your brand from competitors in the crowded Metaverse, enhancing visibility and recognition.
Let us discuss the advantages of registering trademarks in the light of the advent of the Metaverse.
Advantages of Registering Trademarks for Use in the Metaverse
Trademark registration is a must for any company that seeks to enjoy exclusive rights over a mark in a jurisdiction. The law not only protects the trademark in the real world but safeguards it against any infringement in the Metaverse as well. Therefore, just like trademark owners can initiate legal action against the sale of counterfeit products on online stores, they can litigate against infringement in virtual environments. However, it is critical to note that the trademark owner should register the mark for digital goods and services since a trademark for clothing does not extend to virtual clothes.
Moreover, legal protection available after trademark registration is not limited to the class of products and services of trademark registration. A trademark owner can also prevent the unauthorized use of the trademark for unrelated products and services in case the third party is taking undue advantage of or harming the distinctive character or reputation of the mark.
Now that you are familiar with the advantages of registering trademarks in the Metaverse, let us see the process of obtaining a trademark for use in the digital universe.
How to File a Trademark Application for the Metaverse
The process of filing a trademark application for virtual goods is similar to traditional methods but requires additional attention to digital specifics:
Step 1: Check whether or not the trademark is available
Check if your trademark is registrable in the United States. This entails a thorough search of the US trademark registry database to see if any identical or similar trademarks have already been registered.
Step 2: File your application
After ensuring no same or similar marks exist in the trademark database, and gathering all the essential information, file your application with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).
Step 3: Trademark validity check
The Trademark Examiner examines the trademark on numerous grounds.
Step 4: Trademark Office decision and clearance
- If inappropriate information or errors are discovered, a notice is provided regarding the application. A reasonable timeframe is given to the applicant to rectify the data or reapply for application approval.
- In case of no objections, the examiner forwards the form to the Official Trademark Gazette.
Step 5: Opposition
After the trademark is published, other companies and individuals have 30 days to file an opposition to the trademark.
Step 6: Final registration process
If neither the opposition nor the Trademark Examiner raises any objections, the trademark application is eventually authorized and finalized. A ‘notice of allowance’ is also provided. Further, we delve into the methods of trademark protection in the Metaverse.
Trademark-Related Issues in the Metaverse
While mixed and augmented realities have given brand owners access to develop a new industry and customer base, it has also caused problems for trademark owners and users, particularly in the gaming industry. For example, a common problem with the intersection of the virtual and real worlds has been the use of real-world, third-party trademarks in video games that simulate the real world.
An early example of the possible hazards of using real-world trademarks in the virtual world is ESS Entertainment 2000, Inc vs Rock Star Videos, Inc (9th Cir. 2008). The issue, in this case, was whether a virtual representation of a real-life strip club in the famous game ‘Grand Theft Auto: San Andreas’ infringed on the real-life strip club’s logo and trademark rights. The court ultimately decided that the strip club’s depiction in the video game did not infringe on the strip club owner’s trademarks and trade dress rights because the video game was a work of art protected under the First Amendment, and consumers were unlikely to be misled into believing that the strip club created the sophisticated video game.
Many concerns surrounding the use of third-party trademarks in virtual worlds have developed due to the proliferation of user-generated content in recent decades and online “virtual world” games such as Pokemon Go, The Sims, and Second Life. Second Life, for example, a major multiplayer role-playing game with an online economy, allows users to construct their own virtual worlds, develop and market the intellectual property, and even sell their own branded products for profit. Second Life users can even create an online business presence to sell their products in the real world. These advantages, however, come with the danger of unauthorized use of third-party trademarks and potential brand dilution.
Real-World Trademark Challenges in the Metaverse
In the Metaverse, avatars can buy and sell virtual items featuring third-party trademarks, creating new risks for brand owners. As laws around digital trademark use continue to evolve, several cases highlight the challenges faced by trademark owners in virtual spaces:
- Minsky vs. Linden Research, Inc: The plaintiff opened an art gallery named “SLART” in Second Life and registered the trademark with the USPTO. Later, he discovered another user operating “SLART GARDEN” in the same virtual world. The case was settled before a ruling on trademark infringement.
- Leo Pellegrino vs. Epic Games, Inc: Pellegrino, a saxophonist whose dance moves went viral, sued Fortnite‘s creator, claiming a virtual saxophone-playing avatar copied his moves. The court dismissed his privacy and trademark claims, suggesting they were more aligned with copyright law. However, his fraudulent endorsement claim was allowed to proceed, though he eventually dropped the case.
- AM General vs. Activision Blizzard: AM General, the maker of Humvee, sued Activision for featuring the truck in Call of Duty. The court ruled in Activision’s favor, stating that using real military vehicles added artistic relevance and realism, protected under the First Amendment. This case highlights how liability increases when trademarks are used for direct commercial benefit rather than artistic expression.
These cases reveal the legal grey areas surrounding trademarks in virtual environments. As the Metaverse continues to grow, so will the challenges in protecting brands. The next section covers best practices for trademark owners navigating these evolving risks.
Best Practices for Trademark Owners in the Metaverse
As the Metaverse continues to expand, blurring the lines between physical and virtual spaces, trademark owners must adapt to protect their brands. Here are some key strategies to safeguard trademarks in this evolving landscape:
1. Register Your Trademark: Ensure your trademark is registered with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and its foreign equivalents. This offers a presumption of exclusive rights to use the mark with specific goods or services and strengthens enforcement against unauthorized use in both real and virtual worlds.
2. Use Trademark Monitoring Services: Monitoring every potential infringement is challenging, especially with large trademark portfolios. Engaging a trademark monitoring service helps track relevant markets and online content for unauthorized usage. Prompt notifications allow for swift action. Consider assigning a third party to review these reports for efficiency.
3. Report Infringements Promptly: Immediately notify platforms of any infringing activity by third-party users. Most platforms have procedures to remove infringing content quickly to avoid liability, making prompt reporting crucial.
4. Analyze Infringing Use and Legal Claims: Not all uses in the Metaverse are legally actionable. Assess how the infringement impacts your brand and its market. External legal counsel can guide this process. In the U.S., famous brands have additional protections under the Federal Trademark Dilution Act, which addresses unauthorized use that “tarnishes” or “blurs” the trademark, even without consumer confusion.
5. Build a Metaverse Presence: Establishing a presence in the Metaverse can help monitor for infringement while offering new opportunities to engage consumers and boost brand recognition. This proactive approach may also deter potential infringers.
By following these best practices, trademark owners can better navigate the challenges of protecting their brands in the virtual world.
Why Choose Sagacious IP for Trademark Search?
Since trademarks are essential in the real world as well as the Metaverse, it is necessary to conduct a thorough search before registering one to avoid infringement. The following are some of the reasons why Sagacious IP is the ideal trademark search partner for you:
- A dedicated team of over 20 trademark experts with several years of experience.
- Ability to search for existing trademarks that are exact, near-exact, or similar sounding in the same classifications and goods & services.
- Ability to conduct global, cluster-based, and localized trademark searches.
- Proven track record of delivering high-quality services to clients.
- State-of-the-art tools to provide accurate and reliable search results.
- Customised delivery schedules.
- Solutions that are both affordable and effective.
Our trademark experts specialize in providing customized search services to our clients. To create a complete report on these searches, we cover all potential combinations, distinct variations, and phonetically related marks in our trademark search.
Final Thoughts
The aspects of the Metaverse continue to evolve at a rapid pace. It is challenging to develop a corporate strategy in such a volatile environment, characterized by rapid growth and new entrant innovation. The risks and costs of engaging early and consistently in the development of the appropriate intellectual property, developing hypotheses about future business models, and identifying ecosystem partners and collaborators are, on the other hand, relatively low. The asymmetrical risk of being left behind justifies the modest initial investment required to get started and explore this new digital landscape. Brand owners who want to succeed in the Metaverse should think about intellectual property ownership and the risks and benefits that come with it.
At Sagacious IP, our trademark searches provide businesses with accurate, industry-specific trademark insights, helping you make informed decisions. Our dedicated trademark search team ensures you receive comprehensive, timely, and cost-effective reports. Start your journey today—discover how our Trademark Search service can safeguard your brand in the Metaverse and beyond.





